Democracy: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Harrystein (talk | contribs) m (AWB genfixes and CE, added Empty section (2) tag) |
Harrystein (talk | contribs) (+Graphic of Athenian democracy.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
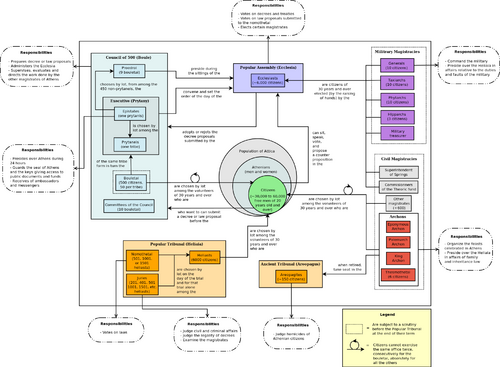
{{redirect-multi|2|Democrat|democratic|the political party in the United States|Democratic Party (United States)}}<!--Add other links, or a disambiguation page, when creating a page for another party of the same name.--> | [[File:Constitution-of-the-Athenians-in-the-4th-century-BC.png|thumb|500px|Detailed representation of the Athenian constitution, ca. 4th century BC. Note the use of [[sortition|selection by lot]], cycling of representatives, large numbers of everyday citizens, and direct participation in the political process.]]{{redirect-multi|2|Democrat|democratic|the political party in the United States|Democratic Party (United States)}}<!--Add other links, or a disambiguation page, when creating a page for another party of the same name.--> | ||
'''Democracy''' (Greek: δημοκρατία, ''dēmokratiā'', from ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people govern themselves, usually by electing bodies of representatives.<ref>https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/democracy</ref> [[Western world|Western]] [[capitalism|capitalist]] society is dominated by [[liberal democracy|liberal democracies]], which [[revolutionary socialism|revolutionary socialists]] criticise as legitimising organs of a [[dictatorship of the bourgeoisie|dictatorship of the capitalist class]] and obstacles against the establishment of meaningful democracy of the masses. | '''Democracy''' (Greek: δημοκρατία, ''dēmokratiā'', from ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people govern themselves, usually by electing bodies of representatives.<ref>https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/democracy</ref> [[Western world|Western]] [[capitalism|capitalist]] society is dominated by [[liberal democracy|liberal democracies]], which [[revolutionary socialism|revolutionary socialists]] criticise as legitimising organs of a [[dictatorship of the bourgeoisie|dictatorship of the capitalist class]] and obstacles against the establishment of meaningful democracy of the masses. | ||
Revision as of 16:42, 2 November 2023

Detailed representation of the Athenian constitution, ca. 4th century BC. Note the use of selection by lot, cycling of representatives, large numbers of everyday citizens, and direct participation in the political process.
Democracy (Greek: δημοκρατία, dēmokratiā, from dēmos 'people' and kratos 'rule') is a form of government in which the people govern themselves, usually by electing bodies of representatives.[1] Western capitalist society is dominated by liberal democracies, which revolutionary socialists criticise as legitimising organs of a dictatorship of the capitalist class and obstacles against the establishment of meaningful democracy of the masses.
Direct and representative democracy
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. |
Applications of democracy
In the state
In political parties
In worker-led enterprises
Other applications
Critique of democracy
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. |
References